Treatment of Portal Vein Thrombosis

In acute and chronic portal thrombosis caused by a disease that makes the blood more likely to clot (a prothrombotic disease), the main treatment is an anticoagulant (medications to prevent more clots from forming).
In acute portal vein thrombosis, the main treatment goals are:
- Prevent the clot from increasing in size.
- Prevent intestinal infarction, which occurs when the intestines do not receive enough blood.
- Try to recanalise the vein (unblock it).
- Prevent portal vein hypertension (increased blood pressure in the portal vein).
In chronic portal vein thrombosis, the goal of anticoagulation is to:
- Prevent the thrombosis from progressing.
- Prevent clots from forming in other parts of the body.
- Assess whether complications of portal vein hypertension that can develop over time should be treated or prevented.
If a specific cause of the thrombosis is detected (such as an underlying disease), it will be evaluated if a specific treatment for that condition is necessary.

Surgery is recommended when intestinal ischaemia is suspected in cases of acute portal vein thrombosis. Intestinal ischaemia occurs when the intestines do not receive enough blood due to the clot, which can lead to the death of intestinal tissue if not treated quickly.
In these situations, surgery is necessary to:
- Remove damaged tissue from the intestines.
- Restore blood flow to the intestines.
- Prevent serious complications such as intestinal perforation or widespread infection (sepsis).
Save the intestine and prevent the condition from worsening in an emergency operation.

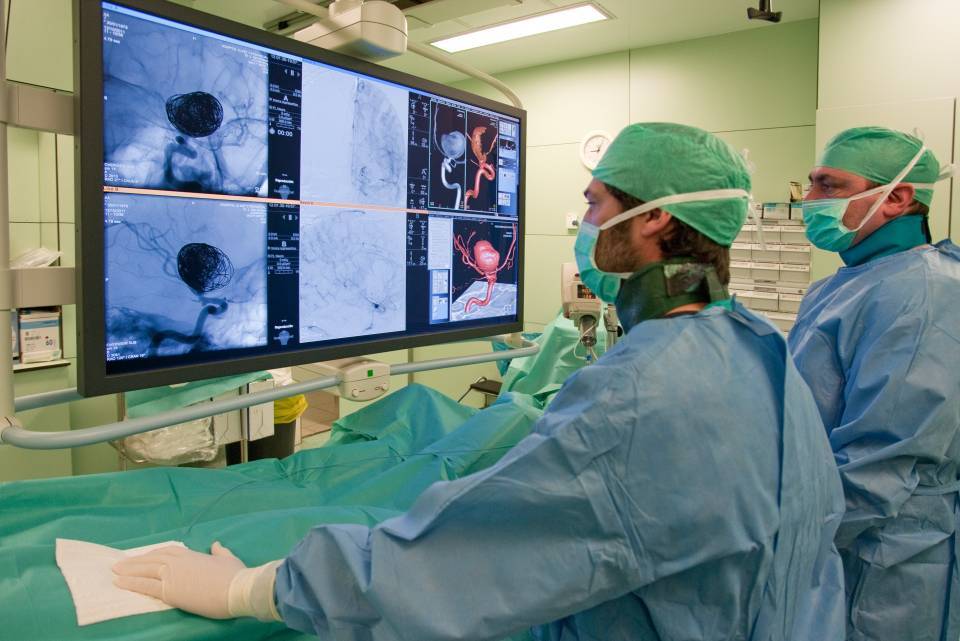
The possibility of performing a portal recanalisation (unblocking) procedure should be considered for patients with chronic portal vein thrombosis with severe complications of portal hypertension that do not respond to treatment; and those with extensive acute portal thrombosis with signs of intestinal damage.
The procedure is performed using interventional radiology techniques, which unblock or form a new path for blood flow through the portal vein.
Key aspects of the procedure:
- Individual assessment. Before performing the procedure, a multidisciplinary team of professionals (e.g. doctors specialising in gastroenterology, surgery, radiology or internal medicine) evaluates each case individually to determine if the operation is appropriate and safe for the patient.
- Interventional radiology techniques. The aim of these techniques is to improve blood flow and reduce pressure in the portal vein by inserting a stent (an expandable mesh to open blocked veins) or forming a shunt (a new path for the blood).
This type of treatment can help control complications associated with portal hypertension and prevent further damage to affected organs.
Substantiated information by:

Published: 19 November 2024
Updated: 19 November 2024
Subscribe
Receive the latest updates related to this content.
Thank you for subscribing!
If this is the first time you subscribe you will receive a confirmation email, check your inbox