Risk factors for Skin Cancer
Risk factors are defined as any personal characteristics or habits, hereditary factors or environmental exposure that increase the likelihood of developing a disease.
The main risk factors for skin cancer are:

Skin type. People with light skin face a greater risk than individuals with darker skin tones. While the risk for those with light skin and blond or red hair is four times greater than for other white people with darker skin and dark hair. This is because dark-skinned people produce better quality melanin (eumelanin) which gives the skin and hair their darker tone. It also protects the skin from ultraviolet radiation. The white-skinned population is 20 more times likely to develop skin cancer than the population with black skin. Nevertheless, it is important to highlight that melanoma does in fact affect all races.

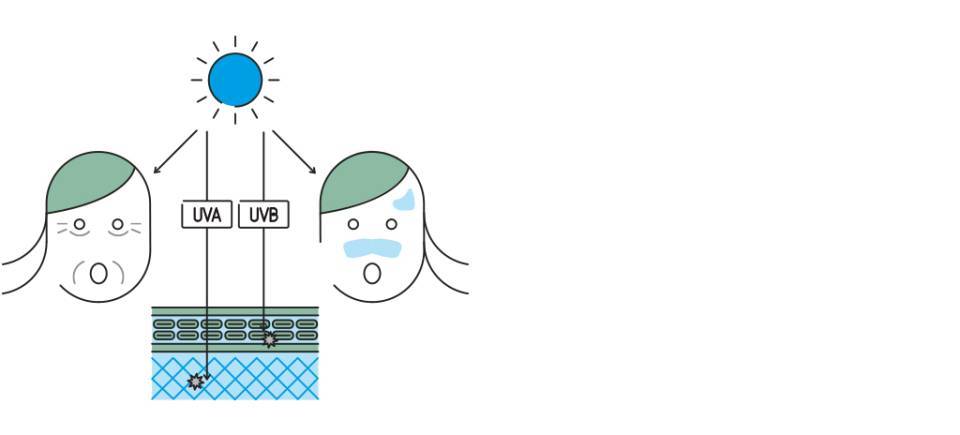
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Regular, intense exposure to UV radiation, whether from the sun or an artificial source (UV lamps), is the main environmental risk factor for skin cancer. It has been shown that repeated, severe sunburns (ones that result in blistering), especially during childhood, increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Light-skinned people who burn easily or have a lot of freckles must be particularly careful when exposed to the sun. Intermittent exposure to intense sunlight, e.g., during summer months, is generally associated with the onset of skin cancer; however, some cases of melanoma are also related to continuous, year-round exposure to the sun, for example, in people who work outdoors.

Personal/family history. The risk of developing a melanoma increases significantly for individuals who have one or more first-degree relatives (parent, sibling or child) with a history of the disease. Approximately 10% of all melanoma patients have a family history of skin cancer.

Genetic mutations. Genetic mutations in skin cells can lead to a lack of control over growth mechanisms and result in skin cancer. Some of these mutated cells can remain dormant and do not grow for several years. That is why they say that the skin has a memory and sunburns can lead to skin cancer years after they occurred.

The immune system. The immune system plays a very important role in controlling and eliminating genetically altered cells. Therefore a decrease in the body’s immune function results in a greater risk of developing skin cancer, especially if the skin has already suffered an accumulation of alterations due to sun damage produced over the years.

Moles. People with a lot of moles are 7–10 times more likely to develop a melanoma. Moles are coloured patches of skin. They may be pinkish, dark brown or the same colour as the rest of the skin. The medical term for a mole is melanocytic nevus (plural nevi).
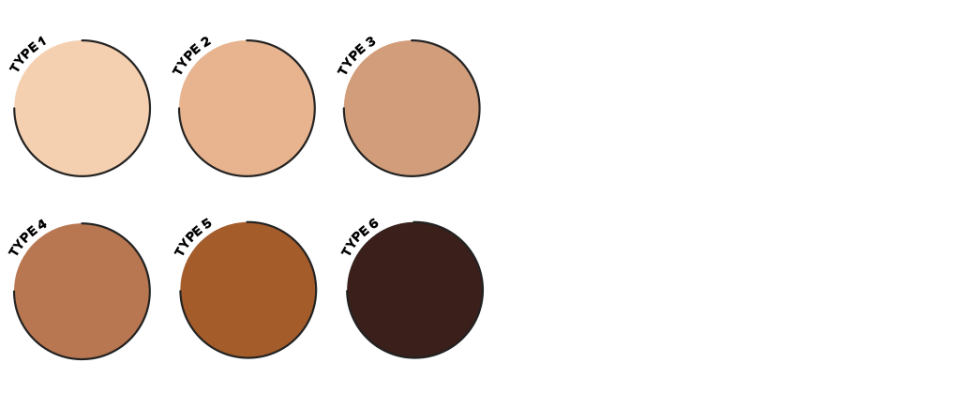
The likelihood of burning and tanning is based on the type of skin and degree of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays. Dermatologists categorise skin type into six subgroups in function of how the skin reacts to UV rays.
These subgroups are called “Fitzpatrick skin phototypes”, in honour of the doctor who created the classification. The majority of Caucasians are type 2 or 3. People with skin phototype 1 and 2 have the greatest risk.
- Type 1: Very pale skin with red or blond hair, light-coloured eyes and lots of freckles. People who always burn and never tan. This group is the most sensitive to sun exposure (fair-skinned people from Northern Europe).
- Type 2: Pale skin with red or blond hair and blue, green or brown eyes. People who tend to burn and do not tan easily.
- Type 3: The typical skin colour in areas of Europe where there is no predominance for a particular colour of eyes. People who sometimes burn and tan gradually.
- Type 4: People with light brown skin who burn rarely and tan easily. The majority of Hispanics, Asians and the Middle Eastern population are type 4 or 5.
- Type 5: Dark brown skin. People who burn very rarely and tan very easily. It is typically observed in people with an Indian heritage and in some Africans.
- Type 6: Black skin. Although it seems people with this skin phototype never burn, they run the same risk as others if exposed to an excessive level of sun.
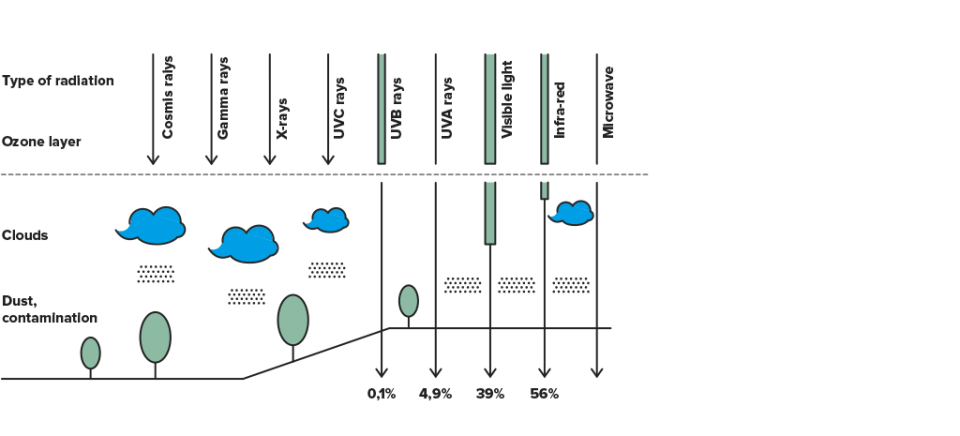
The sun provides the energy needed for life to exist on Earth and is the principal factor in determining the planet’s climate and weather. The sun not only sends visible light to the Earth, but it also emits invisible radiation, which at high doses can have a negative impact on our health.
Solar radiation is comprised of a wide variety of rays; some are blocked by the ozone layer and others manage to reach the Earth’s surface. The radiation that reaches the Earth consists of visible, infrared (IR) and ultraviolet (UV) rays. UV radiation is further divided into UVA, UVB and UVC rays, according to their wavelength. UVC rays are absorbed by the ozone layer.
The intensity of solar radiation depends on diverse factors, such as the time of year, time of day, latitude, altitude, reflections from the Earth’s surface and meteorological conditions.

Height of the sun. The intensity of UV radiation increases as the sun’s altitude increases. Therefore, radiation intensity varies according to the time of day and year. With the exception of tropical regions, UV radiation is most intense when the sun is at its maximum altitude, at around solar noon during summer months.

Latitude. The intensity of UV radiation is greater the closer you are to the equator.

Altitude. The atmosphere is thinner and absorbs less UV radiation at higher altitudes. UV radiation increases by 4% with every 300 metre increase in altitude.v

Cloud cover. Radiation is highest when there are no clouds, but levels can also be high under cloudy skies. Over 90% of radiation can pass through thin cloud coverage.

Ozone. The ozone layer absorbs a portion of the UV radiation that would otherwise reach the Earth’s surface. The thickness of the ozone layer varies throughout the year and even over the course of a day.

Surface reflections. Different types of surface reflect or disperse UV radiation to different degrees. Fresh snow can reflect up to 80% of UV radiation, dry sand on the beach reflects approx. 15% and sea water foam around 25%.
Substantiated information by:


Published: 20 February 2018
Updated: 20 February 2018
Subscribe
Receive the latest updates related to this content.
Thank you for subscribing!
If this is the first time you subscribe you will receive a confirmation email, check your inbox