Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
In the case of erection problems with a vascular origin, it is important to address the risk factors causing the dysfunction. The main factors are smoking, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and a poor diet.

It has been demonstrated that losing weight through the combination of a healthy, balanced diet and regular exercise can improve sexual function.

On the other hand, one of the most significant causes of artery damage is smoking. Giving up smoking is fundamental to limiting vascular damage and provides better long-term results when combined with other treatments.
Treatment with PDE5 inhibitors constitutes one of the pillars of erectile dysfunction therapy, because these medicines are effective, safe and achieve a return to a normal erection in 80% of patients.
The majority of men with difficulties maintaining an erection take oral medication. These medicines work by increasing penile artery dilation and therefore improving blood flow to the penis when sexual desire aroused. The main drugs used are phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors).
There are currently four types marketed in Spain: sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil and avanafil.
- Each drug differs in how quickly it acts and the duration of its effect. The doctor needs to know the patient’s requirements and preferences in order to adapt and customise their treatment.
- Although they are very effective medicines, sometimes they may not be strong enough. In such cases it is important to check that the drug is being used correctly. Treatment failure is often a result of the patient abandoning the therapy.
- Drugs used to treat erection problems are effective and safe. The most frequent secondary effects are headaches (cephalgia), heartburn, facial flushes and muscle pain.
- It is untrue that drugs of this type increase the chance of cardiac events or sudden death; this has been proven in several scientific studies.
The use of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (Sildenafil, Tadalafil, Vardenafil, Avanafil) to treat erection problems is very widespread. These drugs are effective, safe and reinstate normal erection function in around four out of five men.
Nevertheless, the effect may not be obvious after taking the first tablet and it could lead to the mistaken impression that “the tablet does not work”. Explained below is a series of instructions and the main mistakes committed when taking these drugs.
You need to follow a series of rules when taking this type of product:
- You must wait for the recommended period of time established by the manufacturer between taking the drug and feeling its effect to avoid the mistaken assumption that the tablet is ineffective.
- You must take the tablet on four different occasions, on four different days. The first dose may not produce a sufficient effect because you are unfamiliar with how it feels. People are often discouraged by this first “failure”. But you should try the drug on more occasions to find out if it will work for you in general.
- Thirdly, it is very important that you take high doses of the drug before reaching the conclusion that it does not work. High doses of drugs tend to be 20% more effective than low doses. You must try high doses on several occasions before deciding that the drug is ineffective.
- Finally, these medicines often do not work because in fact there is a lack of sexual desire. Men commonly try erection-enhancing drugs when they are not in a sexual situation. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors improve the penis’ response to sexual stimulation, but they do not increase sexual desire.
When drug therapy does not work there are alternatives that can improve blood flow in the penis and therefore increase its rigidity.
These treatments are:

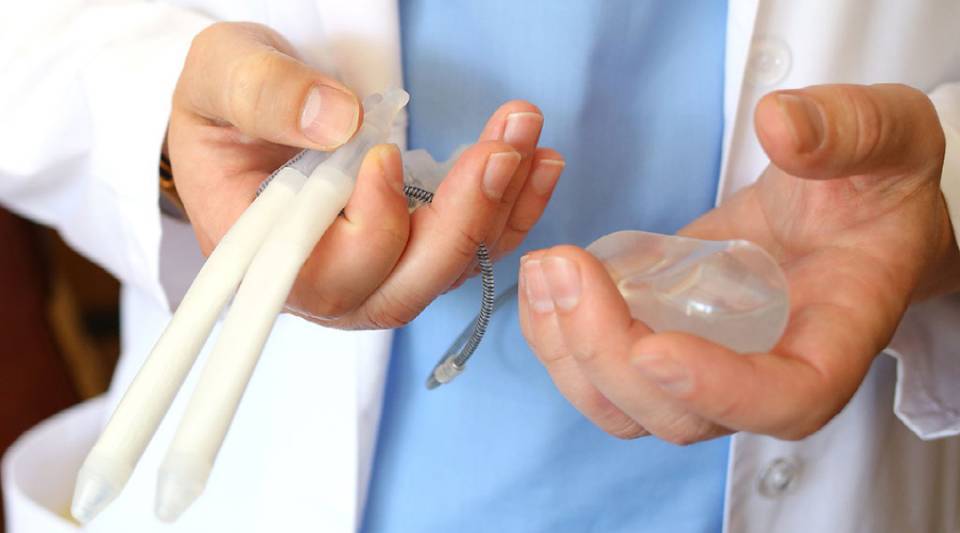
Alprostadil (MUSE®). A urethral suppository which contains alprostadil. An applicator stem is inserted in the urethra (the tube through which urine passes) just after urinating, so the urethra is moist, and then the suppository is released. The drug is absorbed and produces an erection. The effect can be noticed approximately 15 minutes after administration and tends to last for around 1 hour.

Injectable Alprostadil. Alprostadil in a form that is injected into the penis using a very fine needle. The medicine should be administered by the patient or their partner, but it requires some prior training. The injection is effective within a few minutes and its duration depends on the dose.
For both the urethral suppository and injectable alprostadil, it is important to underline if an erection lasts for more than 4 hours it is unusual and requires medical attention.

Suction device. An apparatus which generates a negative pressure on the penis (like a suction cup) and increases the amount of blood flowing into it. After getting an erection, a constrictive rubber band or ring is placed at the base of the penis to keep the blood in; this is then removed after sexual intercourse.
Occasionally, for some cases of erectile dysfunction, a possible solution is to implant a prosthesis.
Penile implants are devices placed inside the penis in attempts to optimise its rigidity when wishing to have sexual intercourse. The implant is inserted through an incision in the scrotum that leaves a scar which is barely visible. The post-operative period is usually short and, after 4 to 6 weeks, the patient can return to sexual activity. The penis’ sensitivity, feeling and orgasm are not affected by the implant.
All forms of erectile dysfunction, including those with a biophysical cause, share psychological components. That is, one way or another, emotional factors can predispose, maintain or aggravate problems with getting an erection.
Sexual therapy is based on a selection of psychotherapeutic techniques adapted to resolve or minimise erectile dysfunction. The aim of sexual therapy for erectile dysfunction is to focus on treating the psychogenic causes and to serve as support for the main drug treatment. In cases that are accompanied by a chronic illness, sexual therapy enables the sexual response to be modified or rehabilitated.
The therapist shall evaluate the full symptomatology to establish the diagnosis and subsequently prepare a customised therapeutic plan. Most sexual therapists believe the partner’s participation is essential to the effectiveness of the treatment. In fact, relationship problems and a lack of communication are often the cause of or can aggravate erectile dysfunction.
The therapist will agree the therapeutic plan, which will include sessions in their office and some tasks to be carried out at home, with the patient and their partner.
Substantiated information by:


Published: 20 February 2018
Updated: 20 February 2018
Subscribe
Receive the latest updates related to this content.
Thank you for subscribing!
If this is the first time you subscribe you will receive a confirmation email, check your inbox