Fever explained in first person
Fever is very common. However, if the person has certain conditions, such as having an organ or bone marrow transplant, perhaps due to chemotherapy or if they recently had surgery or endoscopy, then they must go to A&E as soon as they get a fever.
Fever is the name given to an increase in body temperature. As a parameter, body temperature is perfectly controlled by the thermoregulatory centre located in the brain which acts as a thermostat and indicates the most appropriate temperature for the body given its current conditions.
Normal body temperature is considered to be 36 °C. This temperature is valid for both children and adults, although values of between 35 and 37.5 °C are also considered to be within a normal range. From a clinical perspective, fever is defined as a temperature above 37.7 °C, while high fever is when it rises above 40 °C.
Thermoregulatory centre – the hypothalamus
Our natural thermostat, that is, the body’s thermoregulatory centre, is called the hypothalamus and is located in the very centre of the brain. The hypothalamus detects two temperature signals: one is transmitted by peripheral nerves from the body’s hot and cold receptors, while the other is derived from the temperature of its surrounding blood. These two types of signal are sent to the thermoregulatory centre of the hypothalamus so that it can maintain normal body temperature. In a neutral climate, human metabolism always produces more heat than necessary, thus maintaining the central body temperature at 37 °C. An excess production of heat due to metabolic activity in the muscles and liver is balanced through heat loss in the skin and lungs.
Factors that can affect body temperature are:
- the time of day. In general, body temperature is higher at night.
- a woman’s body temperature can increase by 1 °C or more during the second half of the menstrual cycle.
- physical activity, strong emotions, eating, wearing thick clothes, taking medicines, a high ambient temperature and high ambient humidity can also increase body temperature.
Patients should visit a doctor as a matter of urgency if the fever does not subside within 48–72 hours or underarm temperature measurements exceed 40
Does it occur frequently?
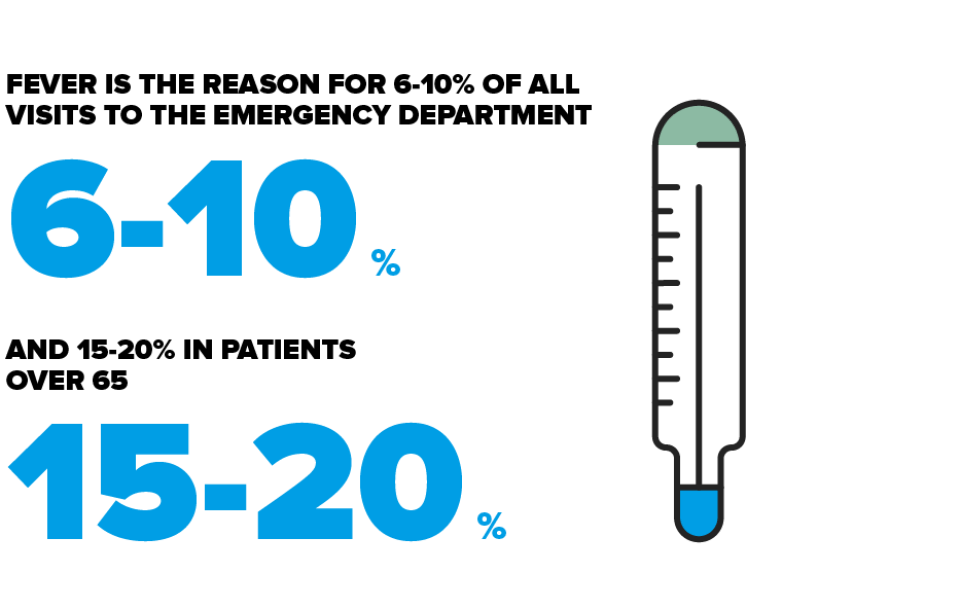
Fever is a common reason for visiting emergency services. Between 6% and 10% of patients who visit emergency services complain of fever and even more so (15%–20%) in the case of patients aged over 65. The severity and consequences vary greatly depending on the feverish patient’s age and underlying condition. Young adults with fever tend to have benign illnesses that usually clear up quite quickly, whereas people aged over 65 or with chronic diseases belong to a group with a high risk of complications.
Substantiated information by:

Published: 20 February 2018
Updated: 20 February 2018
Subscribe
Receive the latest updates related to this content.
Thank you for subscribing!
If this is the first time you subscribe you will receive a confirmation email, check your inbox
Fever related news
29 April 2025
Failure of antibiotics: the three main causes
28 November 2023