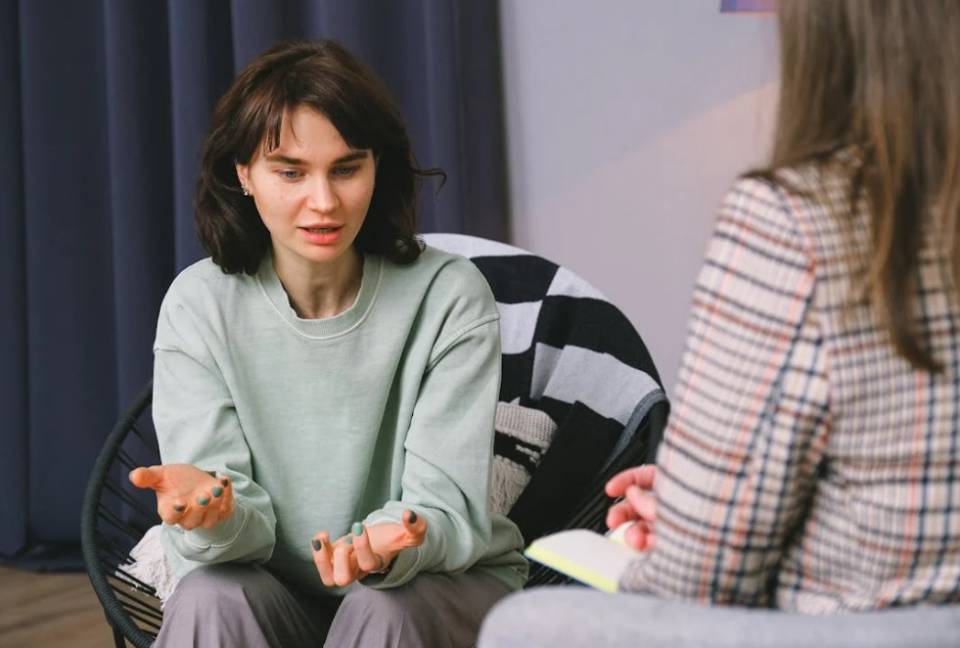
Patient experience, comprehensive management and the training of professionals are the essential factors for creating an effective ecosystem in the care of obesity and related illnesses. This is what emerged from a joint study carried out by the Catalan Health and Social Care Consortium (CSC) and the Hospital Clínic Barcelona, which points to therapeutic education and motivational interviewing as being the main strategies for improving the treatment of this chronic disease, which increases the risk of cardiovascular problems, cancer and diabetes.
The document entitled Estat de situació de l’abordatge de l’obesitat en el context de l’atenció concomitant d’altres malalties cròniques (State of the art of the approach to obesity within the context of concomitant care for other chronic diseases) is the first international guide to a comprehensive approach to obesity and related diseases. The study proposes understanding the patient’s experience, taking care of the whole care process and evaluating the results, going beyond isolated procedures and the generic recommendation to lose weight.
The new care model described by the document introduces the idea that health care must increase value from the patient's perspective: value is defined by those who receive the service—not by those who provide it—which has to be effective and safe, far removed from the concept of "satisfaction", which is subjective and linked to expectations.
Self-management and behaviour change
The joint report by the CSC and the Hospital Clínic Barcelona points to therapeutic education and motivational interviewing as being the main strategies for tackling this problem. Therapeutic education is a learning process that helps people living with chronic illnesses to self-manage their own health. Motivational interviewing encourages changes in behaviour in people who are overweight and obese, and focuses on improving their motivation to adopt healthier habits.
The report concludes that advances in the treatment of obesity and related diseases should be based on four pillars: community resources and policies that allow equitable access to quality care; the power of patients to self-manage their own health; a health system that prioritizes care based on integrated services and continuous improvement; and the training and support of the care team, which focuses on integrating clinical practice guidelines into proactive and collaborative care with patients.
Incidence of obesity
According to the document, Estat de situació de l’abordatge de l’obesitat en el context de l’atenció concomitant d’altres malalties cròniques, prepared with the support of Bias-180 and in collaboration with Novo Nordisk, 21% of adults in Spain are obese and 37% may be obese by 2035. In Catalonia, 13.7% of children 6 to 12 years old and 15.3% of adults suffer from obesity.
The incidence of obesity is significantly higher among Catalans with primary school education (26%) compared to those with university studies (9%). Moreover, 80% of the Spanish population thinks that the management of this disease is their own responsibility, an opinion shared by 19% of health professionals.