Contrary to what many people think, the skin is not the largest organ in the body; it is the digestive tract. The skin measures 2 square metres, but the intestine, if opened out, would occupy 2 tennis courts. The body has 60 trillion cells and the intestine 10 times more, since it contains microbiota, which are microorganisms, mainly bacteria, that produce protective substances. Thus, it is not unreasonable for two-thirds of the immune system to be located in the gut, which is most exposed to pathogens and other microorganisms.
Protective microbiota
The digestive tract is a large, complex organ providing 80% of the body’s defences, and is closely connected to the brain. Some diseases, such as AIDS, caused by the Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV), destroy the intestine’s immune system. In these cases, favourable microbiota can improve their response to infection. Also, in cancer treatment, patients respond much better if they have favourable microbiota; and the same goes for the response to vaccines.
A healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean, which is varied and rich in fibre (plant-based foods) promotes the balance of microbiota; increasing the number of beneficial bacteria and reducing inflammation, which is behind most diseases.
In connection with microbiota, the digestive tract regulates many processes in the body that can affect diseases such as lupus, arthritis and Alzheimer’s, as well as other conditions like anxiety and depression.
What is the difference between probiotics and prebiotics?
When there is an imbalance in microbiota, for example, after taking antibiotics, when there are inflammatory problems or non-specific diarrhoea, it may be recommended to take probiotics.
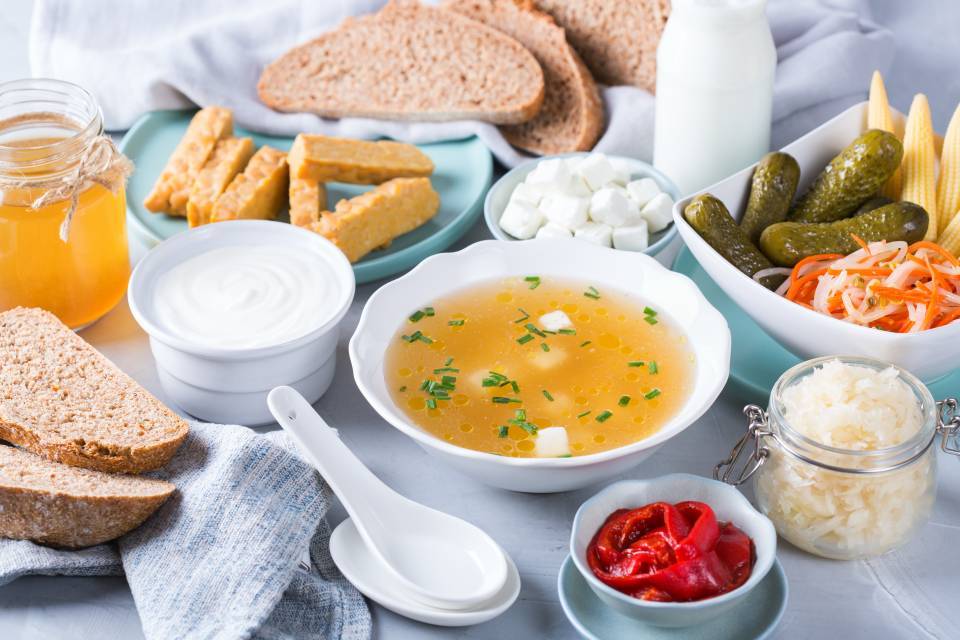
Probiotics are live microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi, found naturally in fermented foods such as kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, pickles, miso soups, tempeh, yoghurt and cottage cheese, which can be taken as a supplement in tablets.
These microorganisms have been shown to be incorporated into the microbiota and offer protection against pathogens. This occurs because they produce substances that fight them. However, for immunosuppressed patients, medical advice is necessary, since the probiotic could behave as a pathogen.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are substances that are ingested through the diet, mainly polysaccharides and oligosaccharides that are ingredients found in foods like cereals, chocolate and dairy products. Some examples are inulin, lactulose and oligofructose, with the latter being found naturally in foods such as wheat, onions, bananas, honey, garlic and leeks.
Information documented by:
Andrea Aira Gómez, microbiologist and doctoral researcher at the Microbiology Unit, Hospital Clínic, Barcelona.