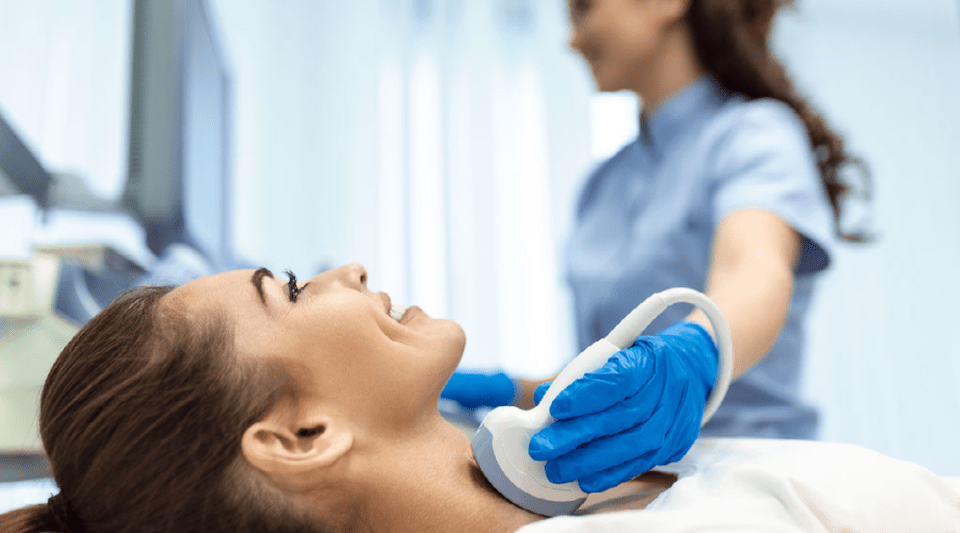
Hyperthyroidism is a disease that occurs when the thyroid gland overproduces thyroid hormones. Its symptoms are very similar to those that occur when an excessive response to stress is generated, so its diagnosis usually occurs in the later stages of the disease.
Its main signs and symptoms are:
- Palpitations and increased heart rate.
- Trembling hands and increased reflexes.
- Anxiety.
- Irritability.
- Increased sweating.
- Difficulty sleeping.
- Increased intestinal transit.
- Increased heat sensitivity.
- Hot, clammy, thin skin.
- Fine, brittle hair.
- Muscular weakness.
- Altered menstrual rhythm.
- Mild to moderate weight loss without loss of appetite.
- Large thyroid.
This disease affects 1% of the general population, and is more prevalent in women; 60-70% of hyperthyroidism cases are due to the autoimmune condition, Graves-Basedow disease (GBD). In this disease, it is the antibodies themselves that cause hyperstimulation of the thyroid gland and make it produce more thyroid hormones than necessary. Other causes of hyperthyroidism are goitre, a pituitary tumour or thyrotoxicosis.
Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed by finding levels of thyroid hormone in the blood higher than normal after performing an analysis. If the person has the disease, it is normal to observe other parameters altered, such as cholesterol, liver transaminases or blood glucose. The reason behind it is that the thyroid is the main controller of metabolism; that is, the internal processes that the body carries out to obtain energy. An ultrasound of the thyroid is also performed to determine the cause and to narrow down the treatment.
The treatment for hyperthyroidism depends on the cause, the severity of the symptoms and the age of the patient. The main treatment relieves the symptoms with drugs that lower the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. If thyroid hormone levels in the blood do not return to normal after pharmacological treatment and the symptoms do not improve, the thyroid is partially or totally removed. This is done surgically to completely remove the gland or by radioactive iodine, which partially destroys it.
The difference between Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism.
Partial or total destruction of the thyroid gland leads to hypothyroidism. This disease is the antithesis of hyperthyroidism, since it occurs when the levels of thyroid hormone in the blood are below normal values. If hyperthyroidism produces an “overexcitation of metabolism”, hypothyroidism “slows it down”. The main symptoms of hypothyroidism are almost the opposite to those of hyperthyroidism:
- Tiredness, fatigue, sluggishness.
- A gloomy mood.
- Memory impairment.
- Sensation of coldness.
- Drowsiness.
- Constipation.
- Pale, dry skin.
- Hair loss and loss of the distal part of the eyebrows.
- Muscle pain.
- Irregular menstruation or increased bleeding.
- Sudden weight gain.
Hypothyroidism is treated by administering synthetic thyroid hormone through pills. Although its treatment is usually chronic, if the correct dose of hormone the person needs to consume is found, they can lead a normal life, usually without associated symptoms.